Podiatrists in Chicago at European Foot & Ankle Clinic treat ingrown toenails, heel pain (plantar fasciitis), foot complications from diabetes, ankle and foot arthritis, nerve problems, tendonitis, hammertoes, flat feet, nail disorders, bunions, warts, fungus, fractures, and sprains.
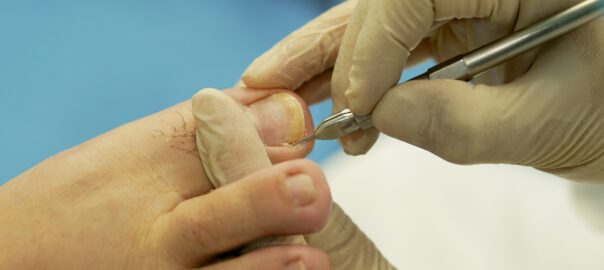
An ingrown toenail, also known as onychocryptosis, occurs when the edge of a toenail grows into the surrounding skin instead of over it. This condition can lead to pain, swelling, redness, and sometimes infection. Ingrown toenails most commonly affect the big toe, but they can occur on any toe.
Causes:
- Improper Nail Trimming: Cutting nails too short or rounding the edges can encourage the nail to grow into the skin.
- Ill-Fitting Shoes: Tight or narrow shoes can put pressure on the toes and push the nail into the skin.
- Trauma: Stubbing your toe or injuring it can lead to the nail growing abnormally.
- Genetics: Some people are more prone to ingrown toenails due to the natural shape of their nails or the structure of their toes.
- Poor Nail Care: Not keeping the feet clean and dry can increase the risk of infection around ingrown toenails.
Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness along the side of the nail.
- Redness and swelling around the nail.
- Inflammation and possible infection with pus.
- Difficulty wearing shoes or walking comfortably.
Treatment and Prevention:
- Soaking: Soak your feet in warm water with Epsom salt for about 15-20 minutes a few times a day. This can help soften the skin and reduce inflammation.
- Proper Nail Trimming: Trim your toenails straight across and avoid rounding the corners. Don’t cut them too short.
- Wear Proper Shoes: Choose shoes that fit well and have enough room for your toes to move comfortably.
- Avoid Trauma: Be cautious to avoid injuring your toes.
- Cotton Under the Nail: If the nail is just starting to ingrow, placing a small piece of cotton or dental floss under the edge can help lift it above the skin.
- See a Doctor: If the ingrown toenail is severe, causing intense pain, infection, or if you have diabetes or circulation problems, it’s important to consult a doctor. They might need to trim the nail or, in some cases, perform a minor surgical procedure to remove a portion of the nail.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is present, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
Remember that if you have diabetes or other medical conditions that affect circulation or immunity, it’s especially important to take care of your feet and seek podiatrist in Chicago advice promptly if you suspect an ingrown toenail by calling: 773-205-0106