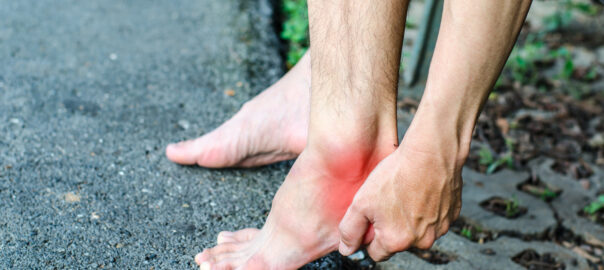
Peroneal tendonitis is a condition characterized by inflammation and irritation of the peroneal tendons in the foot and ankle. The peroneal tendons are located on the outer side of the ankle and are responsible for stabilizing the ankle and assisting with foot movement.
Common causes of peroneal tendonitis include:
- Overuse or repetitive stress: Activities that involve repetitive ankle movements, such as running, walking on uneven surfaces, or playing sports, can strain the peroneal tendons, leading to inflammation.
- Improper footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or do not fit properly can contribute to peroneal tendonitis.
- Ankle instability: If you have a history of ankle sprains or instability, it can increase the risk of peroneal tendonitis as the tendons work harder to compensate for the lack of stability.
- Muscle imbalances: Weakness or imbalance in the muscles around the ankle and lower leg can also lead to peroneal tendonitis.
Symptoms of peroneal tendonitis may include:
- Pain on the outer side of the ankle, which can range from mild to severe.
- Swelling and tenderness around the affected area.
- Increased pain during physical activities or when the foot is dorsiflexed (toes pointing upward).
- A feeling of instability in the ankle.
- Limited range of motion in the ankle and foot.
Treatment options for peroneal tendonitis typically include:
- Rest: Give the affected foot and ankle time to heal by avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Compression and elevation: Using a compression bandage and elevating the foot when resting can also reduce swelling and pain.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen can provide pain relief and reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can recommend exercises to strengthen the muscles around the ankle and improve stability.
- Orthotic devices: Custom or over-the-counter shoe inserts (orthotics) can provide support and help correct any biomechanical issues contributing to the condition.
- Immobilization: In some cases, a brace or walking boot may be prescribed to immobilize the ankle and allow it to heal.
- Corticosteroid injections: In severe cases with persistent pain and inflammation, a healthcare provider may administer corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
Surgery is rarely needed for peroneal tendonitis and is usually reserved for cases that do not respond to conservative treatments or if there is significant tendon damage.
If you suspect you have peroneal tendonitis, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Ignoring the condition can lead to chronic pain and potentially more severe complications.
Call and schedule an appointment with our Chicago podiatrists at 773-769-3310. Our podiatrists can provide a proper diagnosis based on your symptoms, medical history, and potentially recommend imaging studies or other diagnostic tests to identify the underlying cause and determine the appropriate treatment.